Uniaxial geogrids, especially PP (polypropylene) uniaxial geogrids, are an important part of modern civil engineering and construction projects. These geosynthetics are designed to provide reinforcement and stabilization in a variety of applications, including road construction, retaining walls and soil stabilization. Understanding the strength of uniaxial geogrids is critical for engineers and designers to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of their projects.

Composition and structure
PP uniaxial geogrid is made of high-density polypropylene, known for its excellent tensile strength and durability. The manufacturing process involves extruding the polymer into a mesh-like structure, creating a series of interconnected ribs. This design allows the geogrid to distribute loads over a larger area, reducing stress on the underlying soil or aggregate. The uniaxial configuration means that the geogrid is primarily designed to resist tensile forces in one direction, making it particularly effective for applications where loads are applied in a linear fashion.
Strength characteristics
The strength of a uniaxial geogrid is typically measured by its tensile strength, which is the maximum tensile force (pulling force) the material can withstand before failing. This property is critical in determining the performance of geogrids under load. The tensile strength of polypropylene uniaxial geogrids varies widely depending on the specific product and its intended application. Generally, the tensile strength of these geogrids ranges from 20 kN/m to over 100 kN/m, depending on the thickness and design of the geogrid.
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
In addition to tensile strength, other factors such as elastic modulus and elongation at break are also important. The elastic modulus indicates how much the geogrid deforms under load, while the elongation at break provides insight into the material's ductility. A higher elongation at break means the geogrid can stretch more before failure, which is beneficial in applications where ground movement is expected.
Applications and Benefits
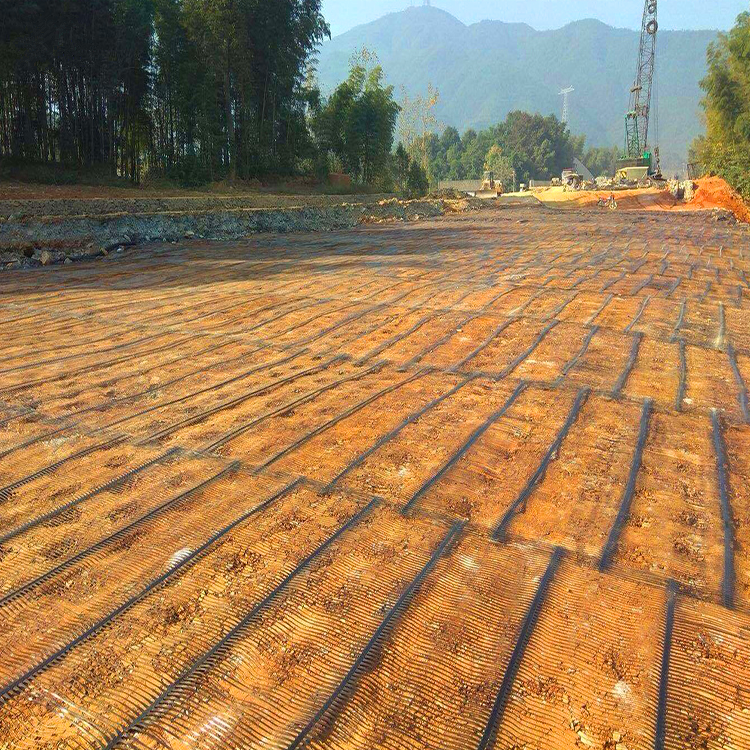
The strength of uniaxial geogrids makes them suitable for a wide range of applications. In road construction, they are often used to strengthen the subgrade layer, improve load distribution and reduce the risk of pavement failure. In retaining wall applications, uniaxial geogrids help stabilize the soil and prevent lateral movement, ensuring structural integrity.
One of the main advantages of using PP uniaxial geogrid is the ability to improve the overall performance of the soil structure. By providing additional tensile strength, these geogrids can significantly reduce settlement and deformation, making infrastructure longer-lasting and more reliable. Additionally, their lightweight nature makes them easy to handle and install, reducing labor costs and construction time.


in conclusion
In summary, the strength of uniaxial geogrids, especially polypropylene uniaxial geogrids, is a key factor in their effectiveness as reinforcement materials in civil engineering applications. Because tensile strengths vary widely, engineers must select the appropriate geogrid based on the specific requirements of the project. By understanding the strength properties and benefits of uniaxial geogrids, professionals can make informed decisions that will improve the durability and performance of their structures. As the demand for sustainable, efficient construction practices continues to grow, the role of uniaxial geogrids in modern engineering will undoubtedly become more important.
Post time: Oct-31-2024